wilcoxon signed rank test coin package|how to interpret wilcoxon signed rank test : distribution sign_test(), wilcoxsign_test(), friedman_test() and quade_test() provide the sign test, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, the Friedman test, the Page test and the Quade test. A general .
webParty of Five. Vudu Seasons 1-6 Amazon Prime Video Seasons 1-6 Apple TV Seasons 1-6. Buy Party of Five on Vudu, Amazon Prime Video, Apple TV. Scott Wolf. Bailey Salinger. Matthew Fox. Charlie.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webVeja ela de quatro mostrando a sua bunda toda aberta exibindo tudo, mostrando sua buceta toda lisinha e sua cuzinho. Veja também mais da sua bunda deliciosa aqui mesmo no .
The wilcoxsign_test function can compute an "exact" p-value when there are zero differences. For example, wilcoxsign_test(c(0,0,0,0,0)~c(0,1,2,3,4), distribution="exact"). The .
It seems to be one is performing Mann-Whitney's U and the other Wilcoxon rank test, which is defined in many different ways in literature. They are pretty much equivalent, just look at the p .Performs one- and two-sample Wilcoxon tests on vectors of data; the latter is also known as ‘Mann-Whitney’ test.Asked 11 years ago. Modified 11 years ago. Viewed 839 times. 0. In R, the function wilcox.test takes the argument conf.level = 0.095 (for example). Giving the same argument to the function .
The first uses the wilcox_test function in the coin package. The statistics reported here are called Z and r . The second uses the wilcox.test function and derives Z from invoking .
sign_test(), wilcoxsign_test(), friedman_test() and quade_test() provide the sign test, the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, the Friedman test, the Page test and the Quade test. A general .Wilcoxon Rank Sum and Signed Rank Tests. Description. Performs one- and two-sample Wilcoxon tests on vectors of data; the latter is also known as ‘Mann-Whitney’ test. Usage. . Wilcoxon signed rank test on paired samples. The Wilcoxon signed rank test on paired sample is a non-parametric alternative to the paired samples t-test for comparing paired data. It’s used when the data are not .
To perform the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test on this data in R, we can use the wilcox.test () function, which uses the following syntax: wilcox.test (x, y, paired=TRUE) where: x, y: two vectors of data values. paired: setting this to .Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric test which is sometimes used instead of the paired Student’s t-test when assumptions regarding a normal distribution are not valid.
The names used for the one-sample Wilcoxon signed-rank test and similar tests can be confusing. “Sign test” may be used, although properly the sign test is a different test. Both “signed-rank test” and “sign test” are sometimes .
However, the wilcoxsign_test in the coin package has the advantage of using the Pratt method to handle zero differences, which may be preferable in some cases. Appropriate data • Two-sample paired data. That is, one-way data with . また、Exact Testは、等分散性を仮定しなくてもいいので適応範囲が広く、その点でもより適切な方法だ。 Wilcoxon Exact Testは、coinパッケージをインストールして、wilcox_test()という関数で実施する。 インストールは最初の一回だけだ。 install.packages . The first uses the wilcox_test function in the coin package. The statistics reported here are called Z and r. The second uses the wilcox.test function and derives Z from invoking the qnorm function. The statistics reported here are called Za and ra. r .Details. The formula interface is only applicable for the 2-sample tests. If only x is given, or if both x and y are given and paired is TRUE, a Wilcoxon signed rank test of the null that the distribution of x (in the one sample case) or of x - y (in the paired two sample case) is symmetric about mu is performed.. Otherwise, if both x and y are given and paired is FALSE, a Wilcoxon .
I'm using the coin-package in R to run comparisons on paired data using wilcoxsign_test. I use the exact version of the test, so I assume that the test goes through all permutations of the paired data and returns an accurate p-value. What is unclear to me is how the z-value returned by default by the function is computed.
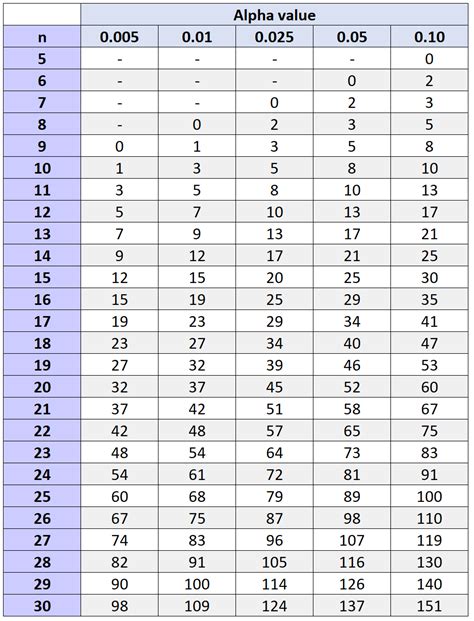
wilcoxon signed rank test table
Compute Wilcoxon effect size (r) for: one-sample test (Wilcoxon one-sample signed-rank test); paired two-samples test (Wilcoxon two-sample paired signed-rank test) and independent two-samples test ( Mann-Whitney, two-sample rank-sum test). It can also returns confidence intervals by bootstap. The effect size r is calculated as Z statistic divided by square root of the .
The wilcox.test function in R is used to perform the signed rank test (for comparing if the median of one sample is equal to a specific value and also paired samples test) and the Wilcoxon rank sum test (also known as the Mann-Whitney U test) for comparing two independent samples to assess whether their distributions are stochastically equal, greater or less than one another.Compute Wilcoxon effect size (r) for: one-sample test (Wilcoxon one-sample signed-rank test); paired two-samples test (Wilcoxon two-sample paired signed-rank test) and independent two-samples test ( Mann-Whitney, two-sample rank-sum test). It can also returns confidence intervals by bootstap. The effect size r is calculated as Z statistic divided by square root of the . Use the Wilcoxon Signed Rank test when you would like to use the paired t-test but the distribution of the differences between the pairs is severely non-normally distributed. The easiest way to determine if the differences are non-normally distributed is to create a histogram of the differences and see if they follow a somewhat normal, “bell .
Compute Wilcoxon effect size ( r ) for: one-sample test (Wilcoxon one-sample signed-rank test); paired two-samples test (Wilcoxon two-sample paired signed-rank test) and independent two-samples test ( Mann-Whitney, two-sample rank-sum test). It can also returns confidence intervals by bootstap.
The effect size r is calculated as .
The coin::wilcoxsign_test() method handles ties using two options: Wilcoxon and Pratt. Let me quote the documentation ("zeros" refer to the ties): For wilcoxsign_test, the default method of handling zeros (zero.method = "Pratt"), due to Pratt (1959), first rank-transforms the absolute differences (including zeros) and then discards the ranks .Performs one and two sample Wilcoxon tests on vectors of data for possibly tied observations. Welcome to SO, Zcjth84! This question may not be a good fit for StackOverflow. (1) There is no code and no data; it seems more conceptual, in which case Cross Validated is a much better fit for the discussion. You might get commentary/answers here (some users traverse both sites), but that's no guarantee. (2) Even if it stays here on SO, then (again) while this site is .One-sample Wilcoxon Signed-rank Test; Sign Test for One-sample Data; Two-sample Mann–Whitney U Test; Mood’s Median Test for Two-sample Data; . The coin package offers a very flexible framework to conduct permutation tests. .
Details. The formula interface is only applicable for the 2-sample tests. If only x is given, or if both x and y are given and paired is TRUE, a Wilcoxon signed rank test of the null that the distribution of x (in the one sample case) or of x - y (in the paired two sample case) is symmetric about mu is performed.. Otherwise, if both x and y are given and paired is FALSE, a Wilcoxon .As such it is often considered to be a non-parametric equivalent for the paired samples t-test. The Wilcoxon Sign-rank test is not the same as the Wilcoxon Rank Sum test (Mann Whitney U test) which is for independent samples. We .The paired samples Wilcoxon test (also known as Wilcoxon signed-rank test) is a non-parametric alternative to paired t-test used to compare paired data. It’s used when your data are not normally distributed. This tutorial describes how to compute paired samples Wilcoxon test in R.. Differences between paired samples should be distributed symmetrically around the median.
The results are tabulated in Figure 1. Based on this data, use the Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test to determine whether there is a difference between the right and left eyes. Figure 1 – Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test for Paired Samples. We perform a two-tailed Wilcoxon Signed-Ranks Test for Paired Samples with α = .05 to test the following null .Calculates r effect size for a Wilcoxon two-sample paired signed-rank test; confidence intervals by bootstrap. I am not a regular R user so I'm struggling a bit on how to get an exact p-value and confidence limits for a single sample using the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test. wilcox.test does not handle ties so it's automatically defaulting to normal approximation, but I have very small samples I am dealing with so need an exact estimate. Previous message: [R] Wilcoxon signed-ranks test using package coin ? Next message: [R] using a variable name stored in another variable? Messages sorted by: Dale Steele wrote: > Given the following data, and hypothesized median M.0 I've found a > method to implement the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. > > Data: (with one zero difference and .
The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric statistical hypothesis test used to compare two related samples, matched samples, or repeated measurements on a single sample to estimate whether their population means ranks differ e.g. it is a paired difference test. It can be applied as an alternative to the paired Student’s t-test also known as “t-test for .The Wilcoxon signed rank test is a nonparametric hypothesis test that can do the following: Evaluate the median difference between two paired samples. Compare a 1-sample median to a reference value. In other words, it is the nonparametric alternative for both the 1-sample t-test and paired t-test. To perform the 1-sample test, analyze the raw . Wilcoxon signed-rank test is defined in R through wilcox.test function (with paired=TRUE) which uses [dprq]signrank functions. Another implementation of MWW/Wilcoxon signed-rank test can be found in the coin package through wilcox_test function. Share. Cite. Improve this answer. Follow edited Apr 13, 2017 at 12:44. Community Bot. 1 . As a software note, the wilcox.test function in R does not return the Z value. If the sample size is less than 50 and there are no ties, by default the software computes the p value with an "exact" method, and doesn't compute a Z value at all. In other cases, the function computes the Z value but doesn't report it.
Introduction. In a previous article, we showed how to compare two groups under different scenarios using the Student’s t-test.The Student’s t-test requires that the distributions follow a normal distribution when in presence of small samples. 1. In this article, we show how to compare two groups when the normality assumption is violated, using the Wilcoxon test.
wilcoxon signed rank test significance
Resultado da Ubisoft Connect not working on PC. I just got the game, but can't add friends because Ubisoft Connect is "temporarily unavailable." I've checked .
wilcoxon signed rank test coin package|how to interpret wilcoxon signed rank test